Unfortunately, pests love them too! Not to worry, we’ve got everything you need to know about who might visit your sunnies for a nibble, including what they look like, and how you can deal with them. We link to vendors to help you find relevant products. If you buy from one of our links, we may earn a commission.
When to Look for What
The list of pests that like to nibble on Helianthus can be a little daunting, but if we break this up into groups of which insects to watch out for during the different plant development stages, it becomes a lot simpler to understand and plan for. Seedlings attract cutworms, wireworms, and sunflower beetles. During the vegetative state, which is when the plant is growing those tall stems and big leaves, keep an eye out for sunflower beetles, thistle caterpillars, and stem weevils. And finally, during flowering and seed development, watch for seed and head clipping weevils, maggots, sunflower midges, sunflower moths, and lygus bugs. Of course, aphids can be a problem at any time. Keep reading to learn more about each of these pests and how to control them.
Aphids
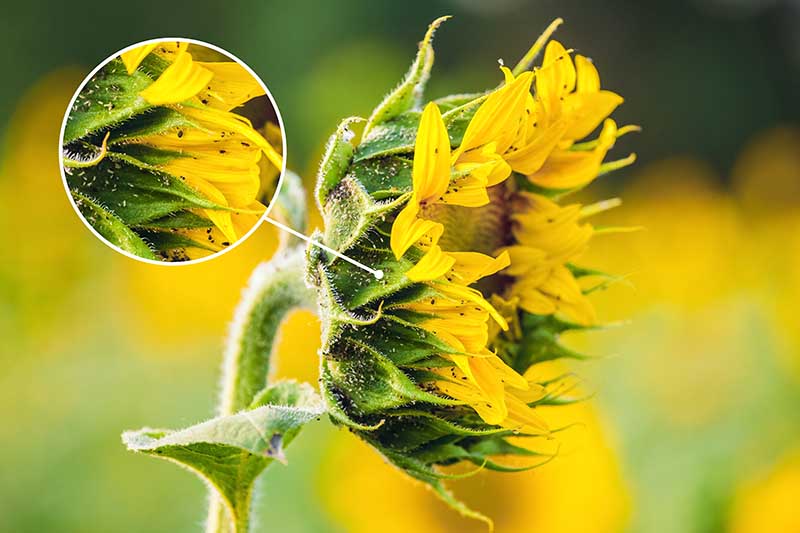
Like many other plants, Helianthus attracts a variety of aphid types, including the melon, peach, and leaf curling plum aphid.
Cutworms
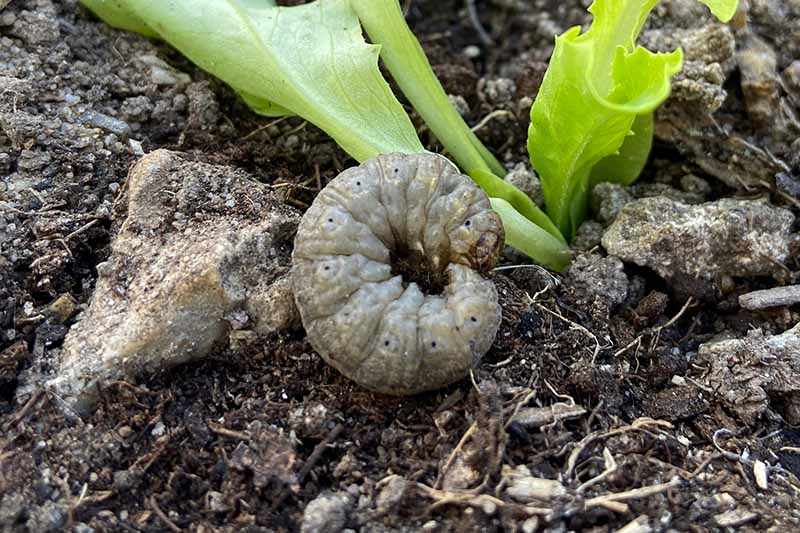
There are several species of cutworms that find new sunflower seedlings delicious. In fact, it is recommended to farmers to plant a border of Helianthus around gardens or fields to attract the cutworms away from other crops. Bonide Insecticidal Soap Insecticidal soaps, such as this one from Bonide that’s available at Arbico Organics, can be effective against aphids and are safe for pollinators if applied correctly. Leaf damage looks like small transparent sections chewed by young larvae, notches, and wilting. But cutworms get their name from their habit of clipping the plant off at the soil line, a very incriminating symptom. Most cutworms feed at night and hide in the soil a few centimeters from the plant. To find them, gently dig the soil around the plant and look for fat, soft, curled brown or gray larvae. Preventative options include weed control, as weeds shelter and feed cutworms before your plants are up. In the fall, work up the soil to expose the larvae and pupae to hungry birds. Handpick the larvae at night after watering or a rainfall, or let your chickens do the work for you. Cutworms love to live in the grass, so leave a three-foot-wide bare soil strip in between your lawn and garden. This makes it harder for the larvae to get to your plants.
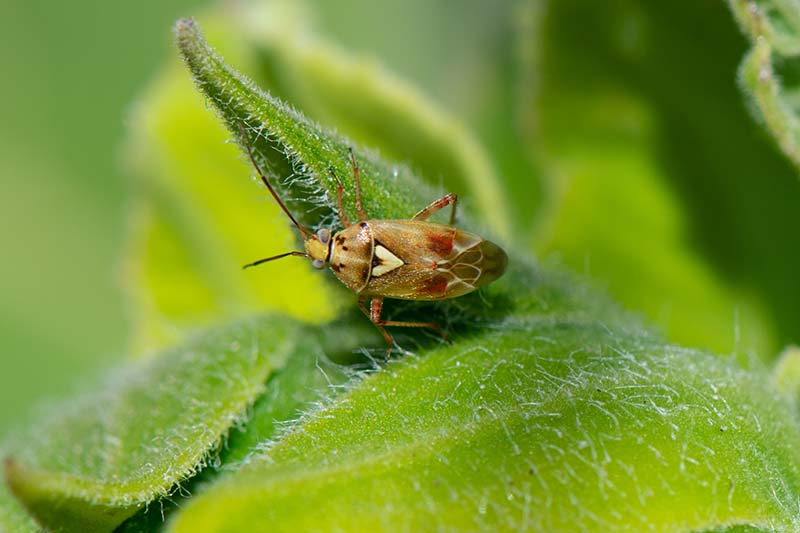
Lygus Bugs
Lygus bugs (Lygus spp.) come in shades of green to red-brown and have a distinctive light-colored triangle at the wing base. You can also spread a layer of diatomaceous earth around the base of each seedling as a fatal barrier. Perm-Guard Crawling Insect Control Try Perm-Guard Crawling Insect Control, available at Arbico Organics. Beneficial nematodes, especially Steinernema carpocapsae, available at Arbico Organics, will attack the larvae in the ground and are safe for everyone involved, including the bees! Monterey Bt Liquid Alternatively, apply a Bacillus thuringiensis product such as Monterey Bt Liquid, available at Arbico Organics. This is another pollinator safe and effective option. Read our complete guide to cutworm control here. Nymphs are green and look like aphids, but are much faster moving and don’t have the aphid’s characteristic “tailpipes” (cornicles). Lygus bugs feed by injecting enzymes that digest plant tissues into the plant and sucking the nutrients out. Feeding on seeds causes brown spots, also known as kernel brown spot, and a bitter taste. It can be a serious problem for farmers and for home gardeners if you plan to harvest seeds for snacks. Lygus bugs can be hard to control because they move quickly so are hard to catch with a spray. If you choose to apply an insecticide in the case of a severe infestation, apply early in the morning when the bugs are less active. Use an insecticidal soap as you would for aphids.
Sunflower Beetles
Zygogramma exclamationis are easy to recognize. They are round beetles with a red-brown head and cream-colored wings covered in reddish-brown longitudinal stripes. The larvae are almost cute, with fat pale green to yellow bowling-pin-shaped bodies. Adult feeding creates shotholes in the leaves, and larvae eat transparent windows into the leaves. Unlike the pests discussed above, sunflower beetles are specific to Helianthus. They are the most damaging defoliator of sunflowers in North America. Normally, beetle numbers are kept in check by beneficial insects in nature. Different types of ladybugs, such as the thirteen-spotted and convergent varieties, eat the eggs.
Sunflower Moths
Homoeosoma electellum can be a serious pest of cultivated sunflowers. The adult moths look like little light brown-gray cigars, and the larvae are brown with longitudinal white stripes. AzaSol Insecticide Planting later in the season can help reduce defoliation. Insecticidal soaps can be effective, as well as neem products such as AzaSol, available at Arbico Organics. The adults are mostly nocturnal, resting under the leaves during the day, and they lay eggs on the flower heads. Watch for dark frass (aka insect poop) and webbing on the flower heads, which indicates the larvae are feeding inside. Young larvae feed on pollen while older larvae feed on the seeds and flower head tissues. Larvae feeding damage increases the risk of infection by Rhizopus fungi, which will rot the flower heads. In the wild, over half of the larvae are parasitized by wasps. Large fields of big headed, cultivated Helianthus provide a huge amount of available refuge for the larvae, rendering the parasitoid wasps less effective. But small plantings like your garden should be well protected by these beneficial insects! Some cultivars of sunflowers don’t produce pollen. This may deter pests that rely on pollen for food during one or more life stages. Read about some of the best pollenless cultivars in this guide. Try a Bacillus thuringiensis product such as Monterey Bt Liquid to treat plants infested with these larvae. Insecticidal soap or neem-based products such as AzaSol are also options.
Sunflower Midges
Contarinia schulzi are tiny midges that lay eggs in sunflower heads, and the larvae feed on the tissues of developing seeds and bracts. This causes low seed production and twisted, gnarled flower heads. Damage is not usually widespread. Delaying planting by a couple weeks can help reduce the risk and severity of potential infestation. Try rotating where you plant your sunflowers each year so you aren’t planting directly into an infested site. Some hybrids are resistant to midges, so keep an eye out for those if these insects have been a problem in the past. Insecticides are not effective since the tiny midge larvae are very well protected inside the sunflower heads.
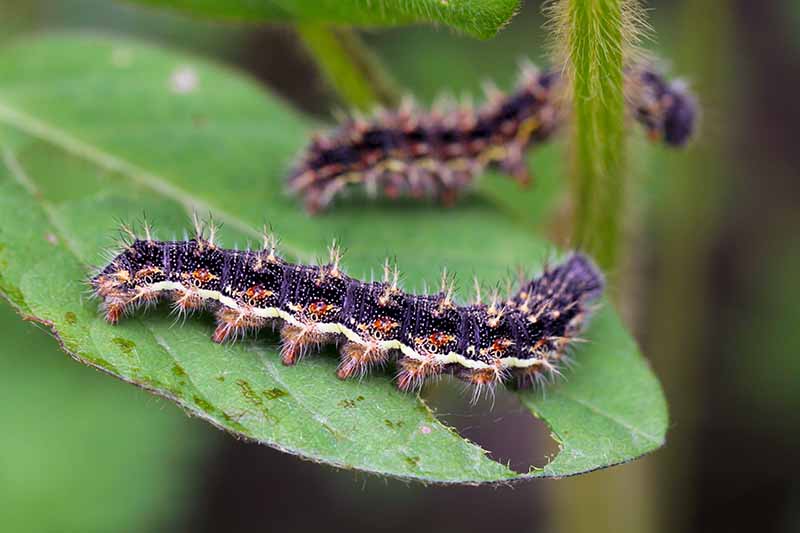
Thistle Caterpillars
The larvae of the beautiful nectar-loving painted lady butterfly (Vanessa cardui), thistle caterpillars adore a good sunflower snack. They come in a variety of colors from light green to black, with a light stripe down both sides, and branching spines all over their bodies. The larvae feed on the leaves, creating irregularly shaped holes, and surround themselves with webbing. Damage is typically minimal and doesn’t warrant treatment, but it is good to know who is chewing on your precious plants. If these pests do become a problem, control them as you would sunflower moths.
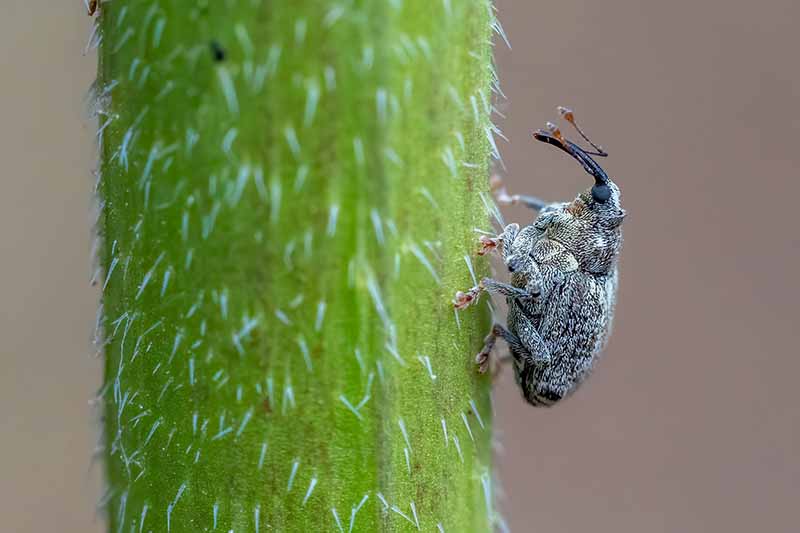
Weevils
There are several different weevils that feed on Helianthus, including the head clipping weevil (Haplorynchites aeneus) and the gray (Smicronyx sordidus) and red seed weevils (S. fulvus). You’ll know a weevil when you see one. They have long snouts, like an elephant! Weevils are pros at playing dead, though, so the adults can be hard to find. Shadows from birds flying over or you rustling through your flower patch can cause them to stiffen and drop off the plant as if they are dead. The head clipping weevil causes damage you won’t be able to miss. They girdle the flower stem or leaf petioles, leaving partially severed heads and leaves hanging sadly on the plant. The gray and red seed weevils, each the color of its name, are the most common damaging pests of Helianthus, with the red weevil being the more common of the two. The adults feed on pollen and lay eggs in developing seeds, which the larvae eat once hatched. The same products that work against sunflower moths will work for weevils. Concentrate application of neem products or insecticidal soaps on the backs of the flower heads. The best time to control sunflower moths and weevils is often overlapping, so you can kill two bugs with one application if both pests are present!
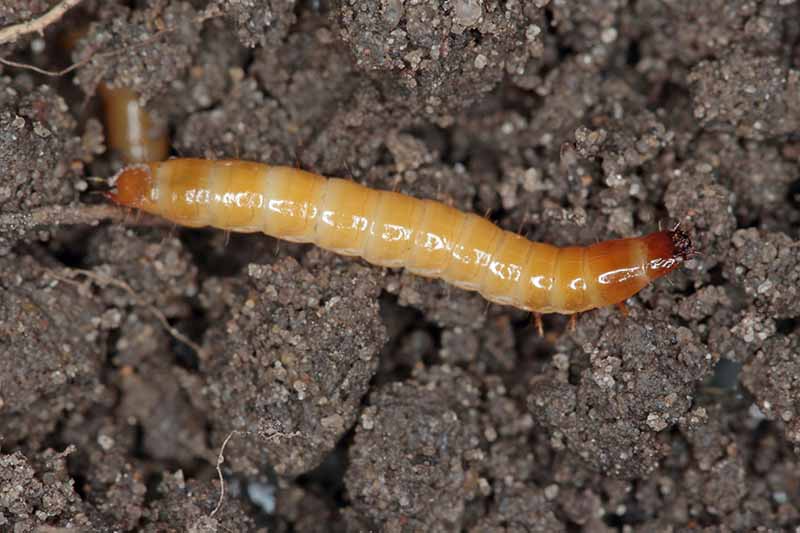
Wireworms and Darkling Beetles
Species from the wireworm family Elateridae, as well as false wireworms from the family Tenebrionidae, all love a sunflower snack. Make sure the product you choose contains the nematode species Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. NemaSeek Hb Beneficial Nematodes NemaSeek Hb Beneficial Nematodes is a good option, and it’s available from Arbico Organics. Adult wireworms are known as click beetles and they come in various colors. Wireworm larvae have a good sense of smell, and move towards the carbon dioxide scent emitted by germinating seeds. They are white to brown, very slender, and have hard, jointed bodies. The larvae feed on the underground portions of the plants, including seeds and roots. As a result, the plant will turn yellow and wilt. False wireworms, or darkling beetles, may also be seen in various colors. Their hard-bodied larvae look very similar to wireworms and come in shiny shades of cream, yellow, or tan. They feed on germinating seeds as well, so it can be hard to tell the difference between the two. For both types of pests, prevent infestations by removing all plant debris from the garden, and tilling to expose the worms to predators. Let your chickens run loose after tilling, or handpick them yourself and put them in a bucket of soapy water. If you see evidence of yellowing, it can be difficult to determine if wireworms are the problem. To trap the worms, try this trick:
Other Pests
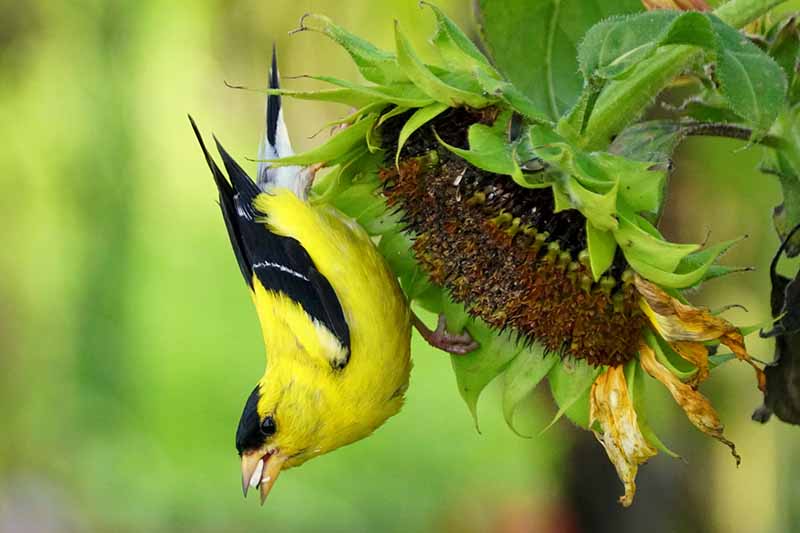
Two other significant and common garden pests that don’t have six legs are birds and squirrels. NemAttack Beneficial Nematodes Try applying beneficial nematodes such as Steinernema carpocapsae, available at Arbico Organics, to control wireworms. Blackbirds, goldfinches, grosbeaks, sparrows, doves, pigeons, and squirrels all love to snack on sunflowers. The high calorie, protein, and fat content of the seeds is attractive to animals that are breeding, storing fat for the winter, or preparing for migration. Check out our article to learn how to protect sunflowers from birds and hungry squirrels. Generally, the small patch or row of sunflowers you grow in your garden won’t see half of these pests, but if they do appear, now you’ve got the know-how to control them! Have you ever had an insect problem on your Helianthus? Tell us about it and how you dealt with it in the comments below, or feel free to reach out with any questions that we haven’t addressed. And once you’re done there, check out these articles next to learn more about growing and using sunflowers:
How to Grow SunflowersIs My Sunflower an Annual or a Perennial?How to Harvest Sunflower SeedsHow to Help Sunflowers That Won’t Bloom