As a dietitian, patients often ask me about taking vitamin supplements to address any potential deficiencies that they may have. Fortunately, we can get the majority of our nutrients from whole foods like fresh produce, rather than relying on pills and powders. Nutrients in the B-vitamin group play several vital roles in maintaining our bodily functions. Many of the vegetables that we eat every day – and may even have growing in our gardens – can supply an ample amount of B vitamins. We link to vendors to help you find relevant products. If you buy from one of our links, we may earn a commission.
What Are B Vitamins?
There are many different B vitamins, each with their own number and name. As a group, they generally support metabolism and energy production. Each of the eight major B vitamins described here has its own unique roles to play in the body as well. Note that there are several other substances in the B family (B4, B10, and B20, for example) but these are not considered to be vitamins and therefore they are not included in this article.
B-Vitamin Breakdown
This portion of the article is broken down into parts, to showcase each of the B vitamins in all of its glory. You’ll learn how each one helps to support our health, and where to find it in the garden. Each vitamin described below also has the DV or Daily Value listed, which is the FDA-defined amount considered sufficient to meet the needs of the general, healthy adult population. If you have specific health concerns, please talk to your doctor about recommended amounts to meet your needs.
B1 – Thiamin
Thiamin is useful in conversion of the food we eat into energy, and helping with nervous system functions.
It also helps to metabolize fats and some types of drugs. Where to find it in the garden: Beans and peas. DV: 1.2 milligrams (mg) daily. One-half cup of black beans contains about 0.4 mg of thiamin.
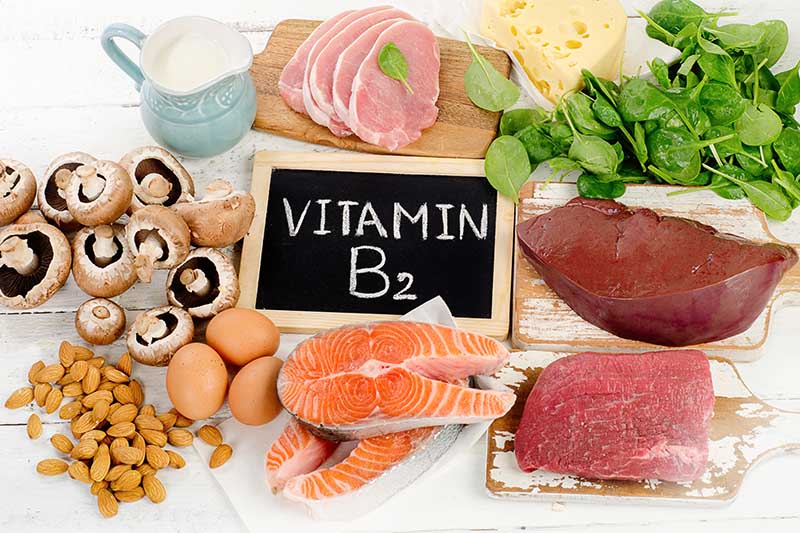
B2 – Riboflavin
Riboflavin helps our bodies to convert food into energy, aids the formation of red blood cells, and assists in overall growth and development.
Where to find it in the garden: Mushrooms and spinach. DV: 1.3 mg daily. One-half cup of grilled portobello mushrooms contains 0.3 mg of riboflavin.
B3 – Niacin
Niacin assists with the production of cholesterol, aids digestion, assists in converting foods into energy, and supports nervous system function.
Where to find it in the garden: Mainly found in meats and whole grains, it can also be found in beans! Raw tomatoes have a small amount of niacin, and more concentrated processed tomato products can be good sources. And yes, we know that tomatoes and a few other “veggies” mentioned in this article are technically fruits, but for the sake of simplicity I’m focusing on what we typically consider to be vegetables in our diet. DV: 16 mg daily. One cup of marinara sauce contains 10.3 mg, and 1/2 cup of lentils contains 1 mg of niacin.
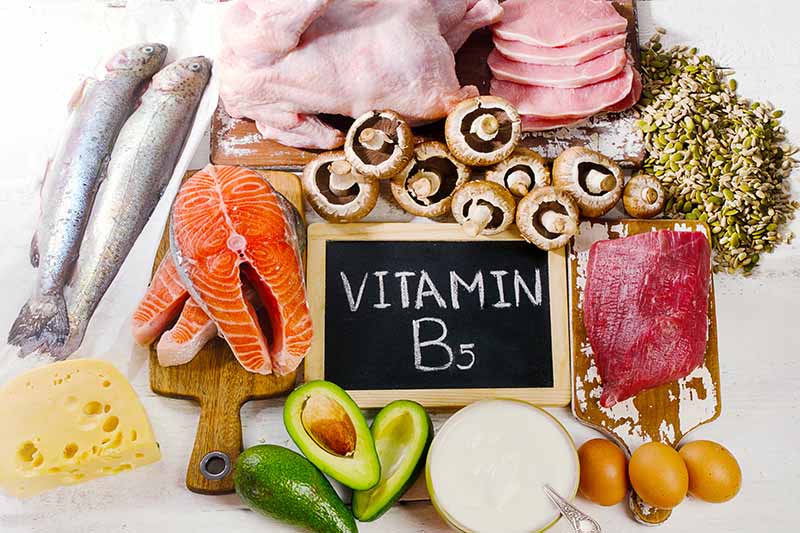
B5 – Pantothenic Acid
B5 plays a role in various processes, including converting the foods we eat into energy (noticing a trend here?), metabolizing fats, producing hormones, and forming red blood cells.
Where to find it in the garden: Peas, beans, broccoli, mushrooms, avocados, and sweet potatoes. DV: 5 mg daily. Half of an avocado contains 1 mg, and 1/2 cup cooked broccoli contains 0.5 mg.
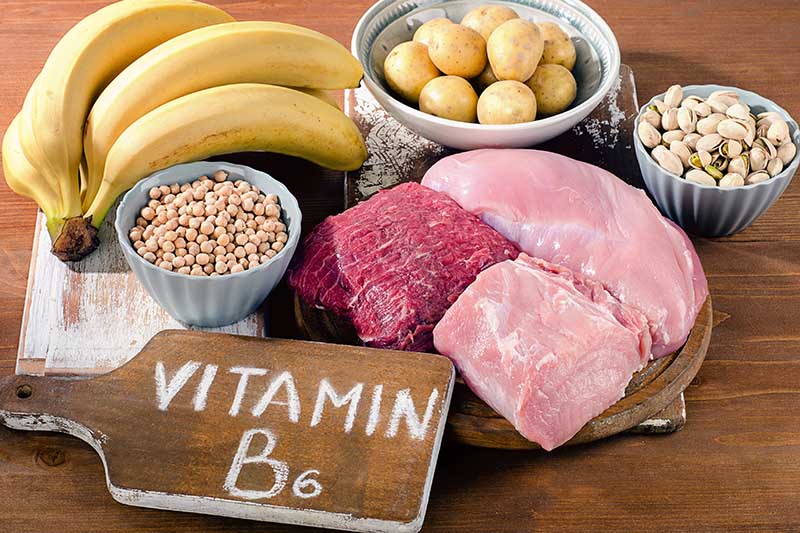
B6 – Pyridoxine
Pyridoxine assists with immune function, nervous system function, metabolism, and red blood cell formation.
Where to find it in the garden: Chickpeas and potatoes. And despite what your parents may have told you, not all of a potato’s nutrients are in its skin. While the skin is the biggest source of fiber, the potato flesh contains over 50% of the nutrients. For the maximum benefit, I still recommend including the skin when cooking. B6 is also found in many fruits, but again, we are focusing on our veggies today. DV: 1.7 mg daily. One cup of chickpeas contains 1.1 mg of pyridoxine – over half your day’s worth!
B7 – Biotin
Biotin plays vital roles in energy storage and metabolism.
Where to find it in the garden: Avocado, cauliflower, sweet potatoes, broccoli, and it’s also found in many fruits. DV: 30 micrograms (mcg) daily. For reference, a microgram is 1/1000th of a milligram. One-half cup of cooked sweet potato has 2.4 mcg of biotin.
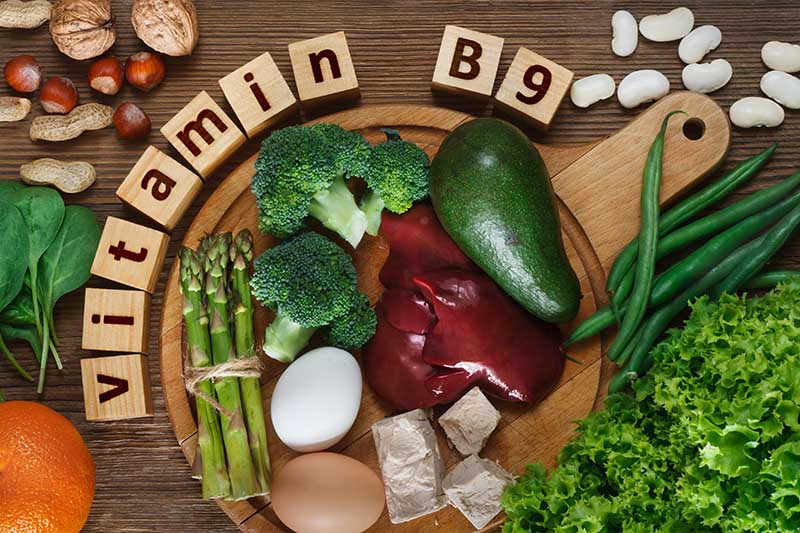
B9 – Folate
Folate aids protein metabolism and red blood cell formation. It is essential in the diets of pregnant women, to prevent birth defects.
Where to find it in the garden: Asparagus, avocado, beans and legumes (notably lentils, black-eyed peas, and pinto beans), peas, and leafy green vegetables. DV: 400 mcg daily. One-half cup of cooked spinach contains 131 mcg, and the same amount of black-eyed peas offers 105 mcg.
B12 – Cobalamin
Cobalamin plays a part in conversion of food to energy, nervous system function, and red blood cell formation. When B12 reaches the small intestine, it combines with a special protein called intrinsic factor that allows it to be properly absorbed.
A lack of this intrinsic factor can result in a condition called pernicious anemia, a type of B12 deficiency. Where to find it in the garden: B12 is difficult to find in plant products outside of fortified cereals. It is produced by bacteria, not plants or animals. Animals are able to retain the B12 produced from bacteria in their gut and store it in their liver and muscles. They may also obtain B12 from eating other animals or animal products. Due to this, the main food sources for humans are meats, seafood, dairy, and eggs. Those following a vegan or plant-based diet are encouraged to take a B12 supplement or add fortified foods to their diet. There are many different forms of B12 – including cyanocobalamin, methylcobalamin, and hydroxycobalamin – that you may see listed on supplements or fortified foods. These forms can all be absorbed by the body and are effective in preventing deficiency. DV: 2.4 mcg daily. Again, you probably will not find this in any garden veggies. A 3-ounce serving of canned tuna fish will give you 2.5 mcg. Some great options for those who follow a plant-based diet (and omnivores as well!) are fortified nutritional yeast or breakfast cereal.
Growing Your Own B-Vitamin Bounty
The B-vitamin family offers plenty of nutritional benefits. Are you interested in upping the vitamin B content of your garden? It can be quite simple to do!
Spinach
First, this ‘Baby’s Leaf Hybrid’ spinach matures in about 30 days, and provides a good source of riboflavin and B6. ‘Baby’s Leaf Hybrid’ Spinach Packets of 300 seeds are available from Burpee. You can read more about growing spinach here.
Potatoes
‘Princess Laratte’ potatoes are a good source of B6, and they also grow well in cooler climates.
‘Princess Laratte’ Potatoes You can find 10 mini tubers ready for planting available at Burpee. Read more about this cultivar and other favorite potato varieties to grow in the home garden.
Broccoli
Broccoli is another B-vitamin powerhouse, containing both biotin and B5. ‘De Cicco’ broccoli seeds can be started indoors or sown directly in your garden.
‘Di Cicco’ Broccoli Find seeds available in a variety of packet sizes from Eden Brothers. Broccoli also freezes well, which can help to extend the nutritional impact of your harvest. Read more about growing broccoli in the garden here.
Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes can be used in both sweet and savory dishes, and are quite simple to grow.
‘Georgia Jet’ To get started, find 12 bare roots for planting available at Burpee. And read more about growing sweet potatoes in the home garden here.
Avocados
Avocados provide folate, biotin, and B5, making them a B-vitamin powerhouse. While many cultivars prefer a warmer climate, there are several that can thrive in cooler climates as well.
Hass Avocado If you’re interested in growing your own, our guide will help! And you can read more about avocado cultivars suited to cooler climates here. To get started with your own avocado tree, you can find the popular Hass variety available at Nature Hills Nursery.
Asparagus
Interested in planting a unique perennial crop? Check out this guide to growing your own asparagus. It can help you to increase your folate intake!
‘UC72’ Asparagus Seeds You can find asparagus seeds in packets of various sizes available at Eden Brothers. Whichever of these veggies you choose to grow, you can feel confident that you’re making an impactful start on meeting your B vitamin needs.
Boosting Vitamin B
Garden-fresh vegetables not only provide incredible flavor, they offer essential nutritional benefits as well. There are many options for getting a variety of sources of B vitamins growing in your garden that you can add to your diet.
What do you plan to grow next to boost your B vitamin intake? Let us know in the comments below! If you’re looking for more information on growing your own nutritious vegetables, check out these articles next:
How to Plant and Grow Zucchini Harvest Hearty Greens from the Garden: How to Grow Kale Healthy Purple Produce: Should You Eat More Purple Fruits and Vegetables?
© Ask the Experts, LLC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. See our TOS for more details. Product photos via Burpee and Eden Brothers. Uncredited photos: Shutterstock. The contents of this article have been reviewed and verified by a registered dietitian for informational purposes only. This article should not be construed as personalized or professional medical advice. Gardener’s Path and Ask the Experts, LLC assume no liability for the use or misuse of the material presented above. Always consult with a medical professional before changing your diet, or using supplements or manufactured or natural medications.